IMCROSS is a simple, scripted method of installing cross-compilers and cross-compiled libraries on a Linux (or possibly other.nix) system, so that you can develop programs targeted to run on Microsoft Windows and Mac OS X at the same time and in the same environment as. Warning: These instructions are for i386 Linux; trying this on x64 Linux has failed. Update 2013-12-13: cross compiling from Linux for macOS no longer works at all for 10.8 and above. The compiler works fine but viable linker tools (cctools for linux) are not available for Linux anymore. That's not currently possible. There's no Mac-Windows cross-compiler & SDK to compile UE4 for Windows from a Mac. You can't build for Mac from Windows either for the same reason. But when I tried to set up QtCreator to cross compile (Tools/Options/Devices) it failed to test connect to my Pi - never had this problem before in previous attempts to set up a cross compiler. Golang supports cross compilation, which generates executable programs on one platform for another. It has been used recently and is very easy to use. Compiling Linux and windows 64 bit executable program under mac CGOENABLED=0 GOOS=linux GOARCH=amd64 go build main.go CGOENABLED=0 GOOS=windows GOARCH=amd64 go build main.go Compiling Mac and windows 64.
│Deutsch (de) │ English (en) │ español (es) │ français (fr) │ magyar (hu) │ português (pt) │ русский (ru) │ 中文(中国大陆) (zh_CN) │ 中文(台灣) (zh_TW) │
- 9From Linux
- 9.1From Linux x64 to Linux i386
- 10From Windows
- 11From macOS (Darwin)
- 12From FreeBSD
- 15Cross compiling the LCL
- 17Cross compile FAQ
Foreword
Note: Before going any further, consider Why not to cross compile? below
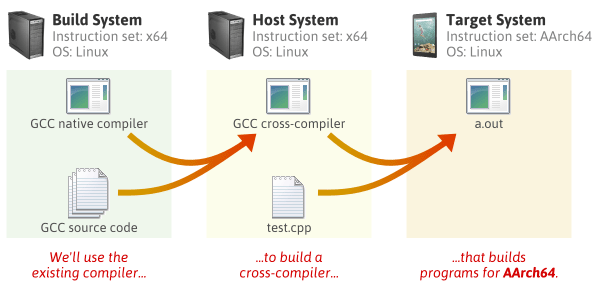
This is a short introduction for newbies. The following sections describe how to setup a system to cross compile, that means creating binaries (executables) for a platform different from the one used for compilation - e.g. working under Linux and creating Win32 executables (or those for FreeBSD or Darwin, etc.). In this case, the platform used for compilation is usually referred to as 'host' (Linux in the example above) and the platform where you want to run your created binaries is your 'target'.
Free Pascal is a compiler and basically converts source into binaries (machine language). These binaries also contain information on how the operating system starts the executables. Moreover, the binaries refer to the APIs provided by the particular operating system, that's why a different implementation of our Run-Time Library is necessary for different operating systems. Therefore these binaries are platform specific. Free Pascal itself does not need much setup. It can create binaries for many platforms. Just tell it to do so.
Host and target on the same CPU
FPC is designed so that the distributed compiler can create machine code for a certain CPU (because different CPUs need different machine code) and it knows specific requirements for all supported platforms (operating systems) available on that particular CPU. This means that you can perform cross-compilation with the same compiler used for native compilation as long as you stick to the same CPU.
Host and target on different CPUs
If you need to create binaries for a different CPU, you need a special cross-compiler, i.e. compiler running on the host platform, but able to create machine code for a different CPU (in the case of FPC, such a cross-compiler would be again able to target all supported platforms available on the _target_ CPU). This cross-compiler is then usually stored in the same directory as the native compiler. Such a cross-compiler may be either compiled by yourself, or you can use a ready made distributed cross-compiler provided for some platforms directly by the FPC team (usually platforms mostly used in portable devices like arm-linux or arm-wince, because these are usually not used as host platforms). FPC binary can then select the right compiler (either the native compiler or the cross-compiler) for the target CPU selected using the -P parameter.
Supported targets
See the Supported target operating systems article for the full list.
Assembler and linker
The compiler is only one part. We also need the assembler and the linker. FPC provides an internal assembler and/or linker for some platforms, but other platforms need external tools. Usually these tools are not able to create binaries for different platforms. That's why we have to use different special linker 'ld' and assembler 'as' for every target platform. These are the binutils.
See Binutils.
Units for target
After creating (or having/installing) the cross tools, one needs FPC RTL and other units compiled for the chosen target platform. For example, every target platform needs a different file system.ppu (System unit), etc. These units may be either compiled using your compiler set up for compilation to the target platform, or you may potentially use officially distributed units compiled (and distributed) with exactly the same FPC version (if available in format usable under the particular host platform).
Configuration
Then your FPC config file will be setup, so that cross compilation becomes so easy, that you can forget all the boring details. The same will be done for the LCL - the Lazarus Component Library (if using Lazarus). And after this you can cross compile Pascal programs for the (different) target platform. The resulting binaries may then be copied to a machine running the target platform, or run under an emulator (e.g. Wine for Win32 binaries under Linux, etc.).
Basic Steps
There are a few common steps involved in cross compiling that you must do in every case:
- Have already a Free Pascal compiler for the platform you wish to compile from.
- You need to have the Free Pascal source code (except for the special case of having everything prepared by someone else).
- You need to either build from source or obtain binaries of the cross-binutils (See Binutils) that run on the platform you are on and are designed to build programs for your desired target platform.
- Sometimes you will need some files from the target you are compiling to.
Cross Compile Arm
From Linux
From Linux x64 to Linux i386
Chances are that your 64 bit Linux distribution is already capable of compiling 32 bit programs but due to the way the FPC build process is designed there are a couple of things you might have to do.
Install libc6-dev-i386 package
On multiarch Debian/Ubuntu you need to install the package libc6-dev-i386
Ubuntu issues
On Ubuntu 20.04 x64, some people have errors like these:
It was solved like this:
- Get cross-libs from fpcupdeluxe: https://github.com/LongDirtyAnimAlf/fpcupdeluxe/releases/tag/crosslibs_v1.2
- Copy from there files 'libglib*' and 'libgio*' to '/lib/i386-linux-gnu'.
- In fpc.cfg, change line
to
Create ld and as files
Check if you already have the files i386-linux-ld and i386-linux-as by doing the following commands:
If you get nothing, it means you need to create them. If you have these files skip to the Compile FPC (see below).
Those are executables files. /usr/bin/i386-linux-ld must contain:
/usr/bin/i386-linux-as must contain:
Both can be created using following commands:
Compile FPC
If for some reason you need to recompile, add the word clean after make (sudo make clean all...). Then:
That's it. Edit your /etc/fpc.cfg file if needed. Note that with 3.0.4 at least, the above crossinstall puts the files in /usr/local/lib/fpc/3.0.4/units/i386-linux and the rest of the FPC systems assumes /usr/lib/... Easily fixed with a symlink but much nicer to do -
Note that if you see messages about failing to find files such as crtn.o and predicted failures to link, its probably because your Linux distro likes to keep its 32bit gcc libraries in /usr/lib32. Check if the missing files are in fact, in /usr/lib32 and, if so, make a small change to your (eg) /etc/fpc.cfg file, around line #177 there is a section that looks like this -
Make it look like this, one additional line -
From Linux to ARM Linux
Information about targeting Linux running on ARM (e.g. Zaurus) may be found in Setup Cross Compile For ARM.
From Linux to Windows
Information on cross-compilation with Lazarus can be found in Cross compiling for Win32 under Linux
From Linux to macOS
Please see Cross compiling macOS on Linux.
From Windows
From Windows to Linux
This is less trivial, there is some info in the buildfaq
See also fpcup for descriptions on which binutils work and what libraries/files to copy.
As the Build FAQ explains, you will need libs (.so files) from the target system, e.g. from /lib and /user/lib (but could be more locations). On some systems, some .so files are actually scripts; check with:
Remove those .so and copy over (or symlink) the .so.x files that you should have to .so in order for the linker to find them.
From Windows to GO32v2
Detailed information may be found in Cross-compilation from Win32 to GO32v2.
From Windows to winCE
- arm-wince describes how to setup a crosscompiler for arm CPU
- i386-wince describes how to setup compiling for i386 CPU (no crosscompiling)
Note: Lazarus installers have an installer that adds Windows to WinCE cross compilation options automatically
From win32 to win64
If you are compiling the 2.1.1 or greater branch of fpc you can just do:
and then
From win64 to win32
Assuming that Lazarus 2.0.10 was previously installed, now install
in the same base directory and then setup your project options to:
- Target OS : Win32
- Target CPU : i386
Failing to set the CPU (Default) lead to incorrect win32-x86_64 platform!
Lazarus guide to cross-compile Win 32/64-bit
Download the installers from sourceforge.net (click on the Files tab):
The installers include FPC and the Lazarus help files (as of Oct. 20, 2019):
- Lazarus 32-bit
- lazarus-2.0.4-fpc-3.0.4-win32.exe
- lazarus-2.0.4-fpc-3.0.4-cross-x86_64-win64-win32.exe
- Lazarus 64-bit
- lazarus-2.0.4-fpc-3.0.4-win64.exe
- lazarus-2.0.4-fpc-3.0.4-cross-i386-win32-win64.exe
To install Lazarus 32-bit, and cross-compile a Windows 64-bit exe:
- Install the win32.exe
- Install the cross-x86_64-win64-win32.exe in the same folder
To install Lazarus 64-bit, and cross-compile a Windows 32-bit exe:
- Install the win64.exe
- Install the cross-i386-win32-win64.exe in the same folder
(The following assumes Lazarus 64-bit with cross-i386-win32-win64)
To cross-compile 32-bit or 64-bit without creating Build Modes:
To Configure Build Modes:
To use Build Modes:
From macOS (Darwin)
You must have the Free Pascal Compiler (FPC) source code already installed. Recent FPC dmg downloads store the source code on macOS in the /usr/local/share/fpcsrc directory.
From macOS to Win32
To be able to compile your Lazarus/Pascal source code on macOS for Windows 32 bit, compile and install the Windows 32 bit cross compiler. To do this you need a bootstrap i386 compiler (ppc386). A Free Pascal Compiler release can always be built by the previously released FPC version, and FPC trunk can always be built by the currently released FPC version. So, as of July 2020:
- to build FPC v3.2.0, you need an FPC v3.0.4 ppc386 i386 bootstrap compiler;
- to build trunk (v3.3.1) you need an FPC v3.2.0 ppc386 i386 bootstrap compiler.
Once you have a bootstrap i386 compiler, then to use that compiler you pass it on the command line with FPC=. For example, to build the trunk (v3.3.1) FPC version cross compiler for Win32:
Now go to the Lazarus IDE and setup the Project Options and Tools Options as follows:
- Project Options
- Config and Target
- Target OS Win32
- Target CPU i386
- Target Processor (Default)
- Target specific options [X] Win32 gui application
- Current LCL widgetset: 'win32'
- Config and Target
- Tools
- Options
- Environment
- Files
- Compiler executable: /usr/local/bin/ppcross386
- Environment
- Options
Once you have setup the Project Options and Tools Options, Lazarus will now be able to cross compile Windows 32 bit applications on your macOS computer. The first time you compile a Windows 32 bit application, Lazarus will also recompile its component source code; so don't be alarmed, it will just take a little longer.
To use the FPC compiler without Lazarus, I use the following shell script:
as follows:
This will create the 32 bit Windows executable in the win32 subdirectory to keep it separate from macOS and Win64 executables. If you do not want to use subdirectories, you can omit the -FEwin32 parameter from the script.
From macOS to Win64
To be able to compile your Lazarus/Pascal source code on macOS for Windows 64 bit, compile and install the Windows 64 bit cross compiler. To do this you need a bootstrap x86_64 compiler (ppcx64). A Free Pascal Compiler release can always be built by the previously released FPC version, and FPC trunk can always be built by the currently released FPC version. So, as at July 2020:
- to build FPC v3.2.0, you need an FPC v3.0.4 ppcx64 x86_64 bootstrap compiler;
- to build trunk (v3.3.1) you need an FPC v3.2.0 ppcx64 x86_64 bootstrap compiler.
Once you have a bootstrap x86_64 compiler, then to use that compiler you pass it on the command line with FPC=. For example, to build the trunk (v3.3.1) FPC version cross compiler for Win64:
Now go to the Lazarus IDE and setup the Project Options and Tools Options as follows:
- Project Options
- Config and Target
- Target OS Win64
- Target CPU x86_64
- Target Processor (Default)
- Target specific options [X] Win32 gui application [win32 is not a mistake]
- Current LCL widgetset: 'win32' [win32 is not a mistake]
- Config and Target
- Tools
- Options
- Environment
- Files
- Compiler executable: /usr/local/bin/ppcrossx64
- Environment
- Options
Once you have setup the Project Options and Tools Options, Lazarus will now be able to cross compile Windows 64 bit applications on your macOS computer. The first time you compile a Windows 64 bit application, Lazarus will also recompile its component source code; so don't be alarmed, it will just take a little longer.
To use the FPC compiler without Lazarus, I use the following shell script:
This will create the 64 bit Windows executable in the win64 subdirectory to keep it separate from macOS and Win32 executables. If you do not want to use subdirectories, you can omit the -FEwin64 parameter from the script.
From macOS i386 to PowerPC
The official FPC installer for macOS/i386 includes a PowerPC cross-compiler and all units necessary to compile PowerPC programs (use ppcppc instead of ppc386 to compile your programs). The instructions below are only necessary if you want to compile and install a new version from svn.
- Compile FPC:
This creates the powerpc cross-compiler compiler (fpc/compiler/ppcrosspcc) and all units. You can install them using the following commands:
Reminder: Universal binaries are created from the individual (i386 and powerpc) binaries using lipo.
From macOS i386 to x86_64
The official FPC installer for macOS/i386 includes an x86_64 compiler and all units necessary to compile x86_64 programs (use ppcx64 instead of ppc386 to compile your programs or use fpc -Px86_64). The instructions below are only necessary if you want to compile and install a new version from svn.
- Compile FPC:
This creates the x86_64 cross-compiler (fpc/compiler/ppcrossx64) and all units. You can install them using the following commands:
If you want to make this newly installed compiler the default version (this is not recommended, and will break your ability to build new FPC 2.7.1 versions without explicitly specifying the path to the latest official FPC release), also execute the following command:
Assuming all of the LCL components your project uses are supported by the Cocoa widgetset, you can compile a Lazarus project from the command line, using a command like this (full path to the compiler seems required):
You can check that your executable is 64-bit uses the 'file' command:
Alternatively, you can set your project to compile as 64-bit using the Lazarus graphical interface:
- Choose the Project/ProjectOptions menu item
- For CompilerOptions/ConfigAndTarget set the 'Target CPU family' to 'x86_64'
- For CompilerOptions/AdditionsAndOverrides store the 'LCLWidgetType := cocoa' in the LPI
Note: Before macOS 10.15 (Catalina), a 64-bit Mac computer could run 32-bit executables. With macOS 10.15 and higher, 32-bit executables can no longer run.
If you want to create a universal binary that executes on a 32-bit Intel as well as in 64-bit mode on a pre-Catalina 64-bit Intel computer you can use the 'lipo' command. This would allow the 64-bit computer to access more memory and in theory might perform a bit better (e.g. different compiler optimizations, more registers though with larger pointers). Assuming you have generated separate 32-bit ('project32') and 64-bit ('project64') executables with Lazarus.
From macOS x86_64 to i386
The official Free Pascal Compiler installer for macOS includes an i386 32 bit compiler and all units necessary to compile i386 programs (use ppc386 instead of ppcx64 to compile your programs or use fpc -Pi386). The instructions below are only necessary if you want to compile and install a new version from svn.
You need a bootstrap i386 compiler (ppc386). A Free Pascal Compiler release can always be built by the previously released FPC version, and FPC trunk can always be built by the current FPC version. So, as at August 2019:
- to build FPC v3.04, you need an FPC v3.02 ppc386 i386 bootstrap compiler;
- to build trunk you need an FPC v3.04 ppc386 i386 bootstrap compiler.
Once you have a bootstrap i386 compiler, then to use that compiler you pass it on the command line with FPC= as below:
And install with:
From macOS to any using fink
The FPC package of the package manager fink has a 64-bit compiler for macOS and cross compilers to Windows, Linux, FreeBSD and others on various CPUs.
Examples for installing a cross compiler are:
or
To compile use these commands:
This command gives the list of cross compilers:
For other platforms (processors and systems) you have to do the setup by yourself. It is basically the same scheme: First, you need the corresponding binutils (see Binutils) and second, the cross compiler and the run time library. Some more details of the building procedure can be learned from the fink package description files of the cross compilers from above.
From FreeBSD
FreeBSD to SPARC
Warning: This section appears to date from around 2005 and may not be relevant anymore. Updates are welcome.
I managed to crosscompile from x86 to Sparc Solaris 9. However the result doesn't work very well, but here is my command-line:
in compiler/ execute:
~/src/sollib is a directory that contains:
- a set of .o's from /usr/local/gcc-3.3-32bit/lib/gcc-lib/sparc-sun-solaris/3.3
- libgcc.a from /usr/local/gcc-3.3-32bit/lib/gcc-lib/sparc-sun-solaris/3.3
- a set of lib*.so from /usr/lib: libaio.so libmd5.so libc.so libelf.so librt.so libdl.so libm.so
Problem is illustrated by the following binary.
I suspect wrong .o's are taken.
From within Docker container
Cross compiling hello world with Docker image and Free Pascal Compiler 3.0.4
1. Pull docker image:
2. Create container with virtual volume based on the pulled image:
a. Identify image ID (first 4 digits are needed):
b. Use the image for the container, map virtual volume from host:
3. Start the container
a. Identify container ID (first 4 digits are needed):
b. Start container:
4. Compile file
a. Copy Pascal file hello.pas from https://github.com/taraworks/lazarus-cross to folder /home/tudi/pascal_files on host
b. Run on host:
b. Attach to container to check the cloned repo is presented:
c. Run on host:
Press 'Enter' one more time and check hello.pas is in container folder. Do not detach with exit from container as container will stop.
c. Compile from container. Change directory to the folder containing hello.pas:
For Windows:
For macOS:
d. Compile from host.
General Unix/Linux notes
Option -XLA is used to rename library dependencies specified in Pascal units. Format is -XLAold=new, to modify ld link option -l<old> to -l<new>.
Option -XR<sysroot> (recent trunk) that can be used to specify the target system root. It's used for:
- adding a prefix to the default added library paths; in the past you used to specify -Xd and these paths manually. E.g. for i386-linux instead of passing /lib, /usr/lib, and /usr/X11R6/lib to ld, it will pass <sysroot>/lib, <sysroot>/usr/lib, and <sysroot>/usr/X11R6/lib to ld.
- detecting the C library (linux specific): glibc or uclibc. E.g. for uclibc detection '<sysroot>/lib/ld-uClibc.so.0' is tried.
Cross compiling the LCL
Since 0.9.31 the LCL is a normal Lazarus package and the IDE will automatically cross compile all needed packages, when you change the target platform of your project.
If something goes wrong, here are some hints that might help to find out why:
Test cross compiler
Test if you have installed the cross compiled FPC correctly:
Create a hello world program test.pas:
And compile it with your source/original platform. Example for x86 Windows:
Then test source compiler:
Replace win32 and i386 with your targets. Example for target Windows 64 bit:
Then test cross compiler:
The program fpc is a wrapper that searches the right compiler (eg ppcrossx64) for the target and executes it.
If this does not work, your cross compiler was not installed correctly. When this works you can cross compile the LCL.
Cross compiling the LCL in Lazarus 0.9.30 and below
If you are sure your cross compiler works, you can do the actual cross compile.
Perform the following steps in the Lazarus IDE to do an LCL cross compile:In older IDEs:
- Set in Tools -> Options -> Environment -> Files the Compiler path to the path to fpc. Normally this is already done.
- Then open Tools -> Configure Build Lazarus.
- Set Target OS (e.g. to Win64) and Target CPU (e.g. to x86_64)
- Click the Build button.
Command line
Apart from the IDE, the command line also allows you to build a cross compiled LCL.
Note: Since 0.9.31 you should use lazbuild to cross compile Lazarus packages. See lazbuild -h for a list of options.
An example: you would cross compile a Windows 64 cross compiler using:
- First thoroughly clean any 64 bit leftovers. This does not touch your 32 bit environment:
- Then build LCL and its required dependencies. We're using LCL_PLATFORM as that presumably corresponds to the widgetset, which is still Windows 32 even on Windows 64 (the widgetsets are the same).
The LCL for your normal OS is untouched.
Cross compiling LCL applications
You first need to cross compile the LCL. See above.
Cross compiling applications means: compiling plus linking. When you have cross compiled the LCL the compilation part is easy. Just set in the compiler options of the IDE the Target OS and Target CPU. The tricky part is the linking. If you cross compile a project you may see something like this:
This means you have to install the graphical libraries of the target system. This has nothing to do with FPC/Lazarus, but with cross compiling a library. Some distributions provides pre compiled packages for this. For example Microsoft provides cross compiled libraries for WinCE for Windows. Under Linux you can install Wine to cross compile from Linux to Windows. Some Linux distributions provide 64bit libraries for 32bit systems.
Cross compile FAQ
Why cross compile?
So you can develop a program for one OS/CPU and compile it for another OS/CPU without rebooting or switching computers.
Why not to cross compile?
In many cases, you will want to test the application which you have cross compiled on its native platform. Compiling the application on that platform in the first place may be easier to set up, especially for new users.
One way of being able to compile and test your application on a non-native platform is to use a Virtual Machine (VM) of that platform on your computer. For example, you could setup a Linux/FreeBSD/Windows VM running on an Apple computer running its native macOS operating system.
There are a number of commercial and free Virtual Machine solutions:
- VMware Fusion for Mac - Host system must be running macOS (Commercial).
- VMware Workstation Player - Host system running Windows 64 bit or Linux 64 bit (Commercial/Free for personal use).
- VMware Workstation Pro - Host system running Windows 64 bit or Linux 64 bit (Commercial/Free trial).
- Parallels Desktop for Mac - Host system must be running macOS (Commercial/Free trial).
- VirtualBox - Host system can be running macOS, Windows, Linux or Solaris (Open Source).
Some, eg Parallels on the Mac, make it trivial to install a desktop Linux operating system with a single click.
Why cross compile from Unix to Windows and not the other way around?
Cross Compile For Mac Versions
See Why Unix to Windows and not the other way around
I want more information on building Free Pascal. Where is it?
There is a general FAQ in pdf format about how to build and configure FPC: buildfaq.
Errors like compiler '/usr/bin/fpc' does not support target arm-linux
Qt Cross Compile
Apart from other causes, this error may occur if you edited fpc.cfg with incorrect options for the cross compiler (e.g. specifying parameters all on one line instead of one per line).
See also
- crossnotes Notes about cross compiling
- GetLazarus - Making it Yourself (Saved copy of 27/09/2016)
Cmake Cross Compile

Comments are closed.